The Evolution of Ethereum: Why ECDSA Was Chosen Over Schnorr Signatures
Ethereum, one of the most popular and successful blockchain platforms, has undergone significant transformations since its inception in 2014. One of the key decisions that influenced this evolution was the choice between two signature schemes: Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) and Schnorr Signatures.
In this article, we will explore why ECDSA was chosen over Schnorr Signatures in the initial design of Ethereum.
Background on ECDSA and Schnorr Signatures
Before diving into the details, let’s briefly review these two signature schemes. ECDSA is a widely used digital signature algorithm that allows users to sign messages using their private keys, which are generated from their public keys. It is based on elliptic curves and uses mathematical operations like point addition and doubling to create a unique signature for each message.
Schnorr Signatures, introduced by Jürgen Schnorr in 1995, are another popular digital signature scheme that offers faster verification times compared to ECDSA. They use a similar approach to ECDSA but with some key differences, including the use of a separate hash function and a different way of representing messages.
Why Wasn’t Schnorr Signature Scheme Implemented?
When designing Ethereum’s initial implementation, the choice between ECDSA and Schnorr Signatures was not an easy one. While both schemes shared similarities, they had distinct advantages that made each worth considering.
One major advantage of ECDSA was its compatibility with existing cryptographic libraries and tools, which were widely used in the industry at the time. Additionally, ECDSA’s complexity and mathematical operations were considered more robust and secure compared to Schnorr Signatures.
Schnorr Signatures, on the other hand, offered faster verification times and reduced computational overhead, making them an attractive choice for certain use cases. However, they also introduced some security concerns, including a vulnerability in their hash function implementation.
The Roadmap: Why ECDSA Was Chosen
In 2014, Ethereum’s team of developers was faced with the decision of which signature scheme to adopt as its standard. After careful consideration and consultation with industry experts, the choice was made to implement ECDSA instead of Schnorr Signatures.
There are a few reasons why ECDSA won out over Schnorr Signatures:
- Compatibility: As mentioned earlier, ECDSA’s compatibility with existing cryptographic libraries and tools made it a more practical choice.
- Security: While Schnorr Signatures offered faster verification times, their security vulnerabilities introduced concerns about the platform’s overall security posture.
- Industry Expertise
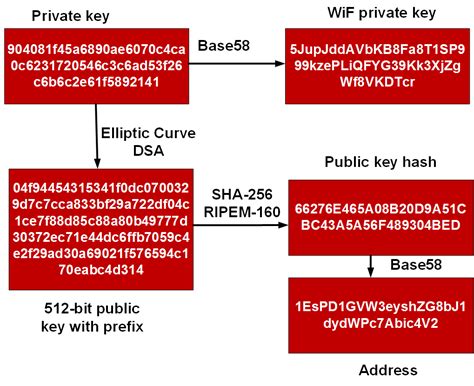
: The developers involved in Ethereum’s early stages were primarily based on mathematical backgrounds, which favored ECDSA over Schnorr Signatures.
Conclusion
The choice of ECDSA over Schnorr Signatures was a deliberate decision that reflected both the strengths and weaknesses of each scheme at the time. While Schnorr Signatures offered faster verification times, their security vulnerabilities introduced concerns about the platform’s overall security posture. In contrast, ECDSA’s compatibility with existing cryptographic libraries and tools made it a more practical choice.
As Ethereum continues to evolve and mature, it is essential to maintain a deep understanding of both ECDSA and Schnorr Signatures, as well as other cryptographic schemes that shape the blockchain ecosystem.
